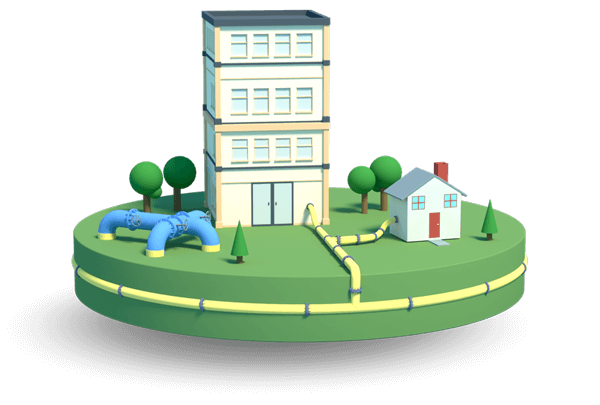
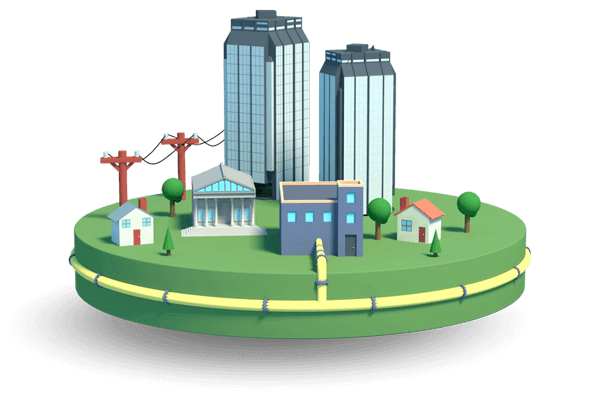
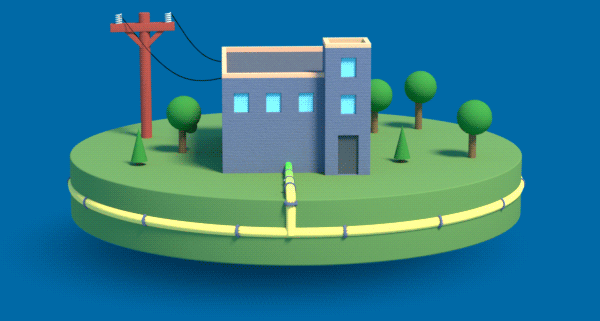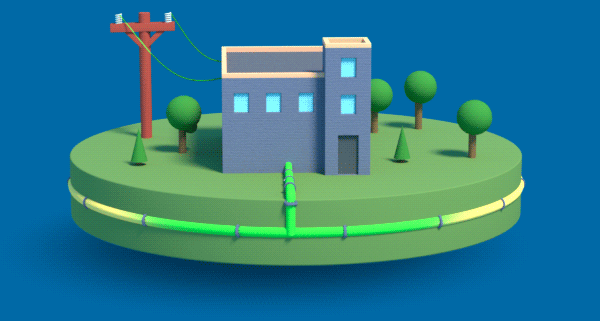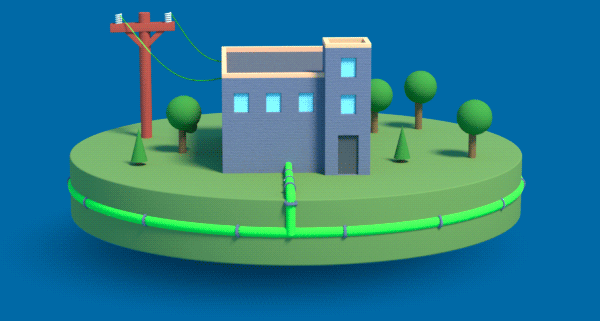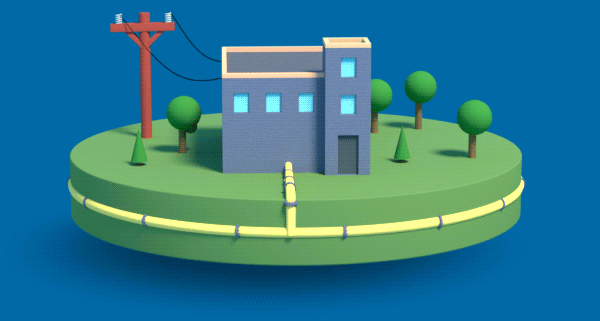
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions means transforming the gas that flows through our underground pipes. We need to move from the traditional natural gas of today to renewable natural gas and low-carbon hydrogen gas.
Low-Carbon Hydrogen Gas
Hydrogen, like electricity, is a flexible energy carrier that can be made from a variety of sources. Hydrogen can be blended with natural gas to lower the carbon intensity of gas. It can be safely used by customers for transportation, home heating, industrial heat or electricity generation. In the future, the natural gas grid can be converted to distribute up to 100% hydrogen. Hydrogen gas can be stored underground in large volumes and distributed in real time to meet our fluctuating energy demands.
Blue Hydrogen is produced from traditional fossil fuels, typically natural gas. The carbon that would usually be emitted is captured and sequestered, resulting in a 90% cleaner energy source than today’s natural gas.

Green Hydrogen is produced from excess renewable electricity, like wind and solar, through a process called electrolysis. When the wind is blowing and the sun is shining, but overall energy demand is low, emission-free hydrogen gas can be produced and stored for when energy demand is higher.
How Does Green Hydrogen Work?
Renewable Gas

While we explore hydrogen technology, Nova Scotia has an opportunity to develop local sustainable and renewable gas projects from organic waste, such as compost, wastewater, landfill waste or wood waste. These projects can start today and will contribute to a stable, circular economy and turn the waste we generate today into the energy we need tomorrow.
How Does Renewable Gas Work?